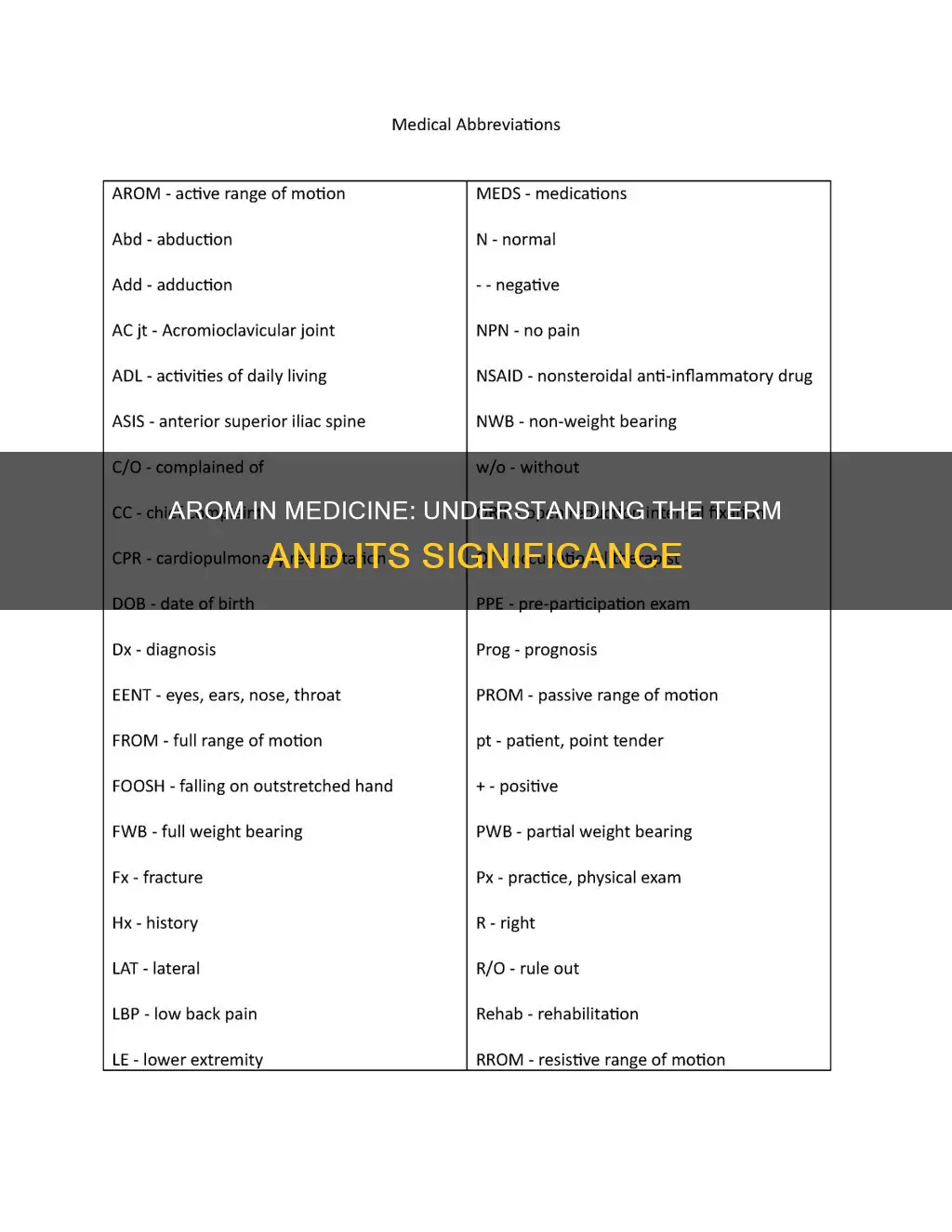
AROM is an acronym for Active Range of Motion, a term used by physical therapists to refer to the extent of movement a patient can achieve without external assistance. It is a category of therapeutic exercises related to joint range of motion. PROM, or Passive Range of Motion, is where a therapist or equipment moves the joint with no effort from the patient.
What You'll Learn

Active range of motion
AROM is an acronym for Active Range of Motion, a term commonly used by physical therapists when referring to the range of movement through which a patient can actively move a joint without external assistance. It is a category of therapeutic exercises related to joint range of motion.
The active range of motion is the range of movement that a patient can perform without assistance. This is in contrast to the passive range of motion, where a therapist or equipment moves the joint with no effort from the patient. The patient performs the exercise to move the joint without any assistance to the muscles surrounding the joint.
AROM exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. Every joint in the body has a "normal" range of motion. Common joint movements include flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
The difference between AROM and PROM (passive range of motion) can be significant, with the neck (cervical spine) providing the motion of the head as a prime example.
Exploring the Finest Aroma-B Cultures: A Sensory Journey
You may want to see also

Artificial rupture of membranes
Amniotomy, also known as artificial rupture of membranes (AROM), is the intentional rupture of the amniotic sac by a healthcare or obstetrical provider. Colloquially, this procedure is known as "breaking the water".
The amniotic sac is a fluid-filled sac that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy, protecting and cushioning it while in the uterus. The fluid within the sac is called amniotic fluid.
There are several reasons why a healthcare provider may recommend AROM. One reason is to speed up labour and encourage dilation of the cervix. Rupturing the membranes may release hormones that cause stronger contractions, and without the amniotic fluid, the baby can move deeper into the pelvis, putting pressure on the cervix and potentially causing further dilation.
Another reason for AROM is to allow for more direct monitoring of the baby's heart rate and health. An internal fetal monitor placed on the baby's head gives a more reliable reading than an external monitor. Additionally, the amniotic fluid can be checked for meconium (the baby's first poop) which can affect the baby's health. Checking for meconium helps healthcare providers plan for suctioning the baby's nose and mouth after delivery.
The procedure is typically performed using a thin, plastic tool called an amnihook, which is inserted through the vagina and used to scratch or tear a hole in the amniotic sac to allow the fluid to escape.
While AROM can be beneficial in certain situations, it is important to note that there are also risks and complications associated with the procedure. For example, umbilical cord prolapse or compression can occur, which can restrict the baby's oxygen supply. There is also an increased risk of infection for the baby without the protection of the amniotic fluid.
The Magic of Aroma Oils: Enhancing Your Daily Life
You may want to see also

Used in physical therapy
AROM stands for Active Range of Motion and is a term commonly used by physical therapists. It refers to the range of movement through which a patient can actively move a joint using the muscles adjacent to the joint, without any external assistance.
AROM is one of the three types of range-of-motion exercises, the other two being Passive Range of Motion (PROM) and Active Assisted Range of Motion (AAROM). PROM involves a physical therapist or equipment moving the joint through a variety of stretching exercises with no effort from the patient. AAROM, on the other hand, is when the patient uses their muscles to complete stretching exercises with the assistance of a physical therapist or equipment.
AROM exercises are often used in physical therapy to improve the range of motion of a joint that has been injured or restricted. These exercises can help strengthen the muscles around a joint, increasing stability and reducing the risk of further injury. They can also increase flexibility, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation and pain.
There are several types of AROM exercises, including straight-plane exercises, rotational exercises, and combination exercises. Straight-plane exercises involve moving the joint in a straight line, such as bending the knee or extending the arm. Rotational exercises involve rotating the joint, such as the shoulder or hip. Combination exercises include a mix of straight-plane and rotational movements, such as reaching overhead and behind the back.
When performing AROM exercises, it is important to do so slowly and carefully to avoid pain. Patients should start with gentle movements and gradually increase their range as tolerated. Warming up beforehand, using a mirror to track progress, breathing deeply, and listening to one's body are all important tips for a safe and effective AROM exercise routine.
Charmed Aroma Candles: Find the Perfect Store for You!
You may want to see also

Used in dentistry
In medical terms, AROM stands for 'active range of motion' or 'artificial rupture of membranes'. In this answer, I will focus on the use of AROM in dentistry, specifically in the context of artificial rupture of membranes.
AROM, or artificial rupture of membranes, is a procedure used in dentistry and medicine to induce or accelerate labour. It involves rupturing the amniotic sac, also known as "breaking the water", to expose the amniotic fluid. This procedure can be carried out by a midwife or obstetrician using a specialised tool, such as an amnihook or amnicot, or even their finger.
The AROM procedure is typically performed when the cervix is partially dilated and effaced, and the fetus is in a vertex presentation, with the head well-applied to the cervix. This ensures that the umbilical cord does not prolapse after the rupture. Fetal monitoring is crucial during this procedure to ensure the baby's wellbeing, and the colour of the amniotic fluid is evaluated to detect any signs of fetal distress, such as meconium staining.
While AROM was once thought to be an effective means to induce labour, recent studies have questioned its effectiveness. A 2013 Cochrane Review concluded that routine amniotomy is not recommended as it showed no shortening of the first stage of labour and a possible increase in caesarean sections.
Despite this, AROM is still performed for several reasons:
- To induce or augment labour by stimulating uterine contractions.
- To monitor the baby's heartbeat internally by placing a scalp electrode against the baby's head, providing a more reliable indication of fetal wellbeing.
- To check the colour of the amniotic fluid for any signs of meconium, which requires additional preparations and personnel.
- To prevent the baby from aspirating the contents of the amniotic sac during birth, which can occur rarely if the sac remains intact.
There are certain criteria that must be met for AROM to be performed, including:
- The mother should have no contraindications for vaginal delivery.
- The mother should be in labour or have a valid indication for delivery.
- The fetal head should be engaged (0 station or more) to prevent umbilical cord prolapse.
In conclusion, while AROM may have applications in dentistry and medicine, recent evidence has questioned its effectiveness in inducing labour, and it should be used judiciously with careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits.
Wonder Woman's Armor: Uncovering a Fatal Weakness
You may want to see also

Used in obstetrics
In obstetrics, AROM is an abbreviation for "artificial rupture of membranes", also known as amniotomy. It is a procedure used to intentionally rupture the chorioamniotic membranes to induce or augment labour. It is typically carried out by a midwife or obstetrician using a specialised tool, such as an amnihook or amnicot, or their finger.
There are several reasons for performing an amniotomy. Firstly, it can be used to induce or accelerate labour by stimulating uterine contractions and increasing their strength. Secondly, it allows for more direct monitoring of the baby's heartbeat by placing a scalp electrode against the baby's head, providing a more reliable indication of fetal well-being. Thirdly, it enables the doctor or midwife to check the colour of the amniotic fluid for the presence of meconium, which may indicate fetal distress. Finally, it can be performed to avoid the baby aspirating the contents of the amniotic sac during birth.
The procedure is generally considered safe if the presenting part is well-applied to the cervix, and the fetal vertex is not floating. Fetal monitoring is used to evaluate the colour of the amniotic fluid and detect any signs of fetal distress. However, there are risks associated with the procedure, including prolonged rupture of membranes, higher rates of infection, and cord prolapse.
The appropriate timing of artificial rupture of membranes is debated, as earlier rupture may lead to longer exposure to ruptured membranes during labour, potentially increasing the risk of infection. Some studies suggest that early amniotomy may not decrease the risk of cesarean delivery but can shorten the time to delivery without increasing the risk of infection or neonatal infectious complications.
Melty Beads: A Creative Alternative to Aroma Beads?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
AROM stands for Active Range of Motion. It is a term used by physical therapists to refer to the range of movement a patient can achieve without external assistance.
PROM stands for Passive Range of Motion. PROM is when a therapist or equipment moves a joint through its range of motion with no effort from the patient. AROM is when a patient moves a joint without assistance.
AROM can also stand for Artificial Rupture of Membranes, which occurs during childbirth.







