Aromatherapy, or the use of essential oils, has gained traction in recent years, with many people turning to it for its therapeutic benefits. However, despite their natural origins, aroma oils are not without their risks. The safety of essential oils depends on various factors, including age, health status, and medication use. In this article, we will explore the potential benefits and hazards of using aroma oils, providing guidelines for safe usage.
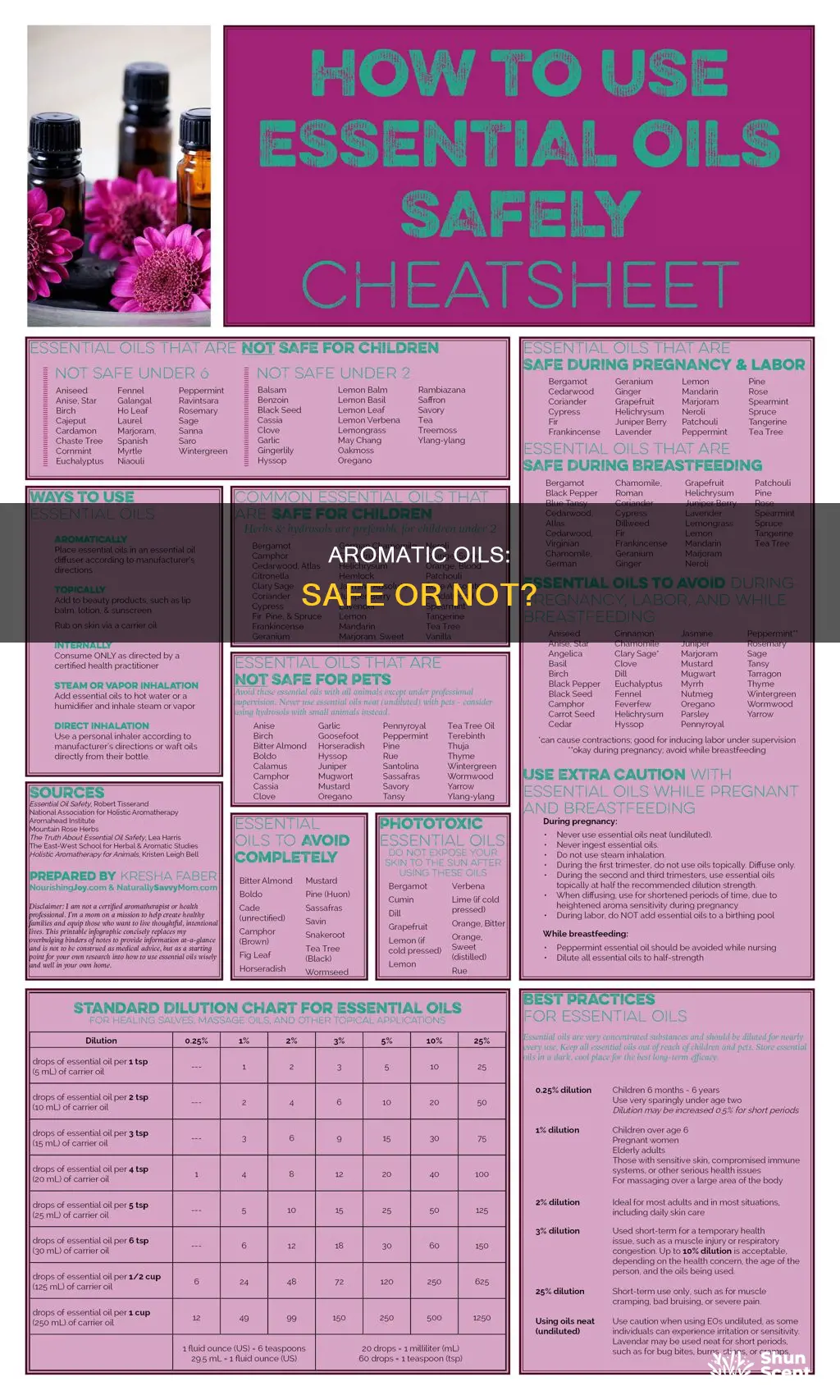
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Safe for ingestion | No |
| Safe for inhalation | Yes |
| Safe for topical use | Yes, but must be diluted |
| Safe for children | No |
| Safe for pregnant people | No |
| Safe for pets | No |
| Safe for ingestion by pets | No |
| Safe for topical use by pets | No |
| Safe for inhalation by pets | No |
What You'll Learn

Aroma oils are safe when diluted
Aroma oils can be safe when diluted and used with caution. Essential oils are highly concentrated plant extracts, and even natural substances can be irritating, toxic, or cause allergic reactions if not used correctly.
Undiluted essential oils should not be applied directly to the skin, as they can cause severe irritation or sensitization. It is recommended that essential oils are diluted with a carrier oil, such as vegetable, almond, jojoba, or coconut oil, to a solution that is 1% to 5% essential oil. This helps to protect the skin and prevent adverse reactions. For children or the elderly, a 1% dilution is recommended.
A patch test is advised before using a new essential oil. This involves applying a small amount of diluted oil to the forearm and covering it with gauze. If a rash, itching, blistering, or swelling occurs, the oil should not be used.
It is also important to buy essential oils from a reliable source, as pure oils are more likely to be safe. The label should include the Latin name of the plant, information on purity, and the country of origin.
In addition to topical use, essential oils can be used in aromatherapy through inhalation or diffusion. However, diffusion should be done in a well-ventilated area, and it is recommended to diffuse in intervals of 30 to 60 minutes on, followed by 30 to 60 minutes off.
Some essential oils, such as lavender, chamomile, and rosewater, are known to have calming and relaxing effects. However, it is important to note that essential oils can interfere with hormones and can be dangerous if swallowed.
Overall, when used with caution and in diluted forms, aroma oils can be safe for adults and children over the age of three.
Exploring Aroma Sexuality: Scents and Sensuality
You may want to see also

Don't ingest aroma oils
Aroma oils, or essential oils, are highly concentrated plant extracts. They are commonly used in wellness, beauty, and cleaning routines. However, it is important to exercise caution when using essential oils as they can be harmful if used or ingested incorrectly. Here are several reasons why you should not ingest aroma oils:
Risk of Poisoning
Misuse of essential oils can lead to serious poisoning. Many essential oils can cause rashes if applied directly to the skin, and some can be poisonous if absorbed through the skin or swallowed. For example, swallowing pennyroyal oil can be highly toxic to the liver, and aspirating essential oils can lead to pneumonia.
Lack of Regulation
Essential oils are not consistently regulated, and the labels may not accurately reflect all the ingredients in the product. This makes it difficult to know exactly what you are ingesting and increases the risk of adverse reactions or toxicity from other ingredients.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to essential oils are possible, and ingestion may lead to severe reactions, especially if you are allergic to any of the ingredients. The most common type of allergic reaction is a skin rash, but more serious reactions, such as difficulty breathing, can occur and should be treated as a medical emergency.
Interaction with Medications
Essential oils may interact with medications and affect their effectiveness. For example, peppermint oil can change how the body absorbs the cancer drug 5-fluorouracil. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before using essential oils, especially if you are taking any medications.
Potential Toxicity for Children
Children have thinner skin and less developed livers, which makes them more susceptible to the toxic effects of essential oils. Even small amounts of certain oils, such as birch and wintergreen, can cause serious problems in young children due to the presence of chemicals like methyl salicylate.
In summary, it is important to treat essential oils with caution and avoid ingesting them. Always consult a healthcare professional or trained aromatherapist before using essential oils, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Aroma Diffusers: Why Less Mist is More
You may want to see also

Aroma oils can be toxic
Firstly, essential oils should not be ingested. They are not regulated, and the label may not list all the ingredients in the bottle. Ingesting certain oils, such as wintergreen, can be deadly. Ingesting other oils, such as eucalyptus, nutmeg, and sage, can cause serious complications like seizures.
Secondly, essential oils can be poisonous if absorbed through the skin. Some essential oils, such as cinnamon, citrus oils, and nutmeg, can cause rashes, burns, and skin irritation if applied undiluted to the skin. Others, like orange, lime, and lemon, can cause phototoxicity if applied before sun exposure.
Thirdly, essential oils can be dangerous if inhaled by children. For example, a child under 30 months old may become agitated if exposed to peppermint oil.
Finally, essential oils can cause allergic reactions, especially in people with atopic dermatitis or a history of reactions to topical products. Reactions can include a red, itchy rash, hives, or breathing problems.
To use essential oils safely, it is important to always dilute them with a carrier oil, like almond, jojoba, or coconut oil, and to perform a patch test before use. Oils should be purchased from reputable sources and stored in dark glass bottles, out of the reach of children.
Aroma Yin Yoga: A Relaxing, Sensory Yoga Experience
You may want to see also

Aroma oils can cause allergic reactions
Allergic contact dermatitis is a common reaction to essential oils, characterised by skin itching, redness, and scaling. This can occur when essential oils are applied directly to the skin or inhaled. In some cases, allergic contact dermatitis can be delayed, with symptoms appearing 12 to 72 hours after exposure. This makes it important to perform a patch test before using a new essential oil, to ensure you don't have a reaction.
Some essential oils, such as citrus oils, can also cause phototoxicity if applied before sun exposure. This can result in skin redness or discolouration.
It is also important to note that essential oils should not be ingested, as this can be dangerous. If you experience any adverse reactions to essential oils, discontinue use and seek medical advice if necessary.
To avoid allergic reactions, it is recommended to dilute essential oils with a carrier oil, such as almond, jojoba, or coconut oil. This helps to reduce the concentration of the essential oil and can prevent irritation.
Additionally, it is important to purchase essential oils from reputable sources and store them safely out of reach of children and pets.
Aroma Decor Fragrances: Safe or Not?
You may want to see also

Aroma oils are flammable
Aroma oils, or essential oils, are highly flammable and should be handled with care to prevent fires. Essential oils are derived from plants and contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can easily ignite under certain conditions. While these oils have a range of household uses, from skin application to air diffusion, their flammability poses a safety risk that users should be aware of.
Factors Affecting Flammability
The flammability of essential oils is influenced by several factors, including the type of oil, its purity and concentration, and the presence of external agents. Oils with low flashpoints, or the temperature at which they vaporize and ignite, are more likely to catch fire. For example, clove, cinnamon, and thyme essential oils have notably low flashpoints, making them highly flammable. However, even oils with higher flashpoints can still catch fire quite easily.
Additionally, the presence of additives and carriers can alter the flammability of an oil. Heat and sunlight can also degrade essential oils over time, impacting their flashpoint and making them more susceptible to ignition.
Safety Measures
To ensure safe handling and storage of essential oils, it is important to take the following precautions:
- Store oils in a cool, dark place, preferably in airtight containers made of glass or metal. Avoid using plastic containers as the oil can break them down over time.
- Always dilute essential oils with a carrier oil when applying them to the skin. Undiluted oils can cause skin irritation and increase the risk of flammability.
- Keep oils away from open flames, candles, stoves, and other direct heat sources.
- Never ingest essential oils as they are meant for external use only.
- Use a high-quality diffuser designed specifically for essential oils.
- Keep essential oils out of the reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or spillage.
In conclusion, while essential oils have a variety of benefits, it is important to respect their flammable nature and take the necessary precautions to ensure safe usage and storage.
Creating Soothing Aromatherapy Blends with Essential Oils
You may want to see also







