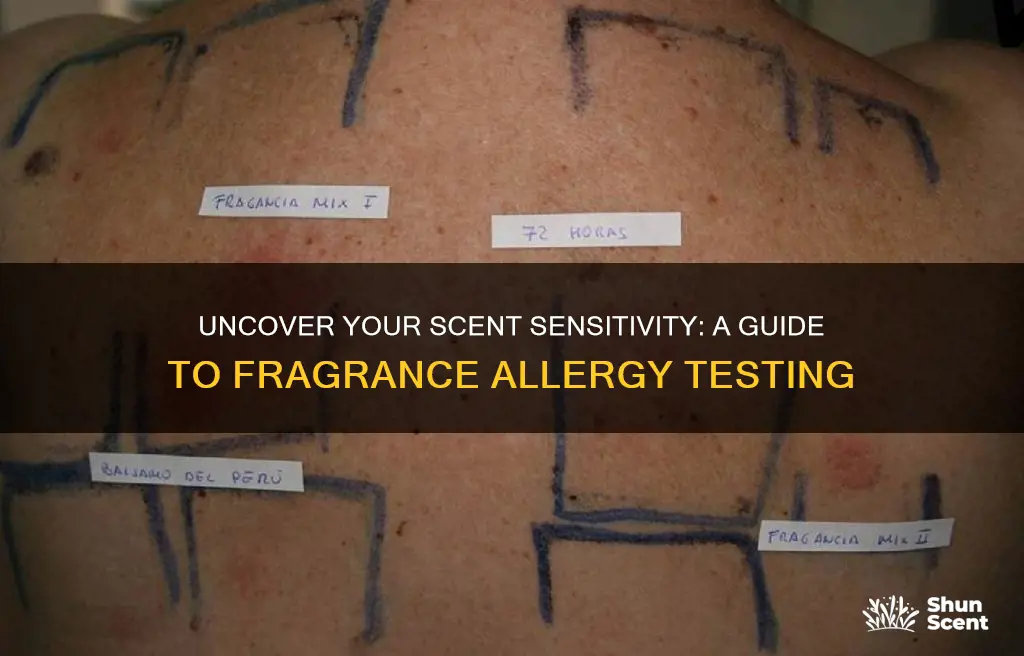
Testing for fragrance allergies can be a crucial step in identifying and managing potential skin reactions. This guide will explore various methods to help you determine if you have a sensitivity to certain scents. From patch testing to self-monitoring techniques, you'll learn how to safely and effectively assess your body's response to different fragrances. Understanding these methods can empower you to make informed choices about the products you use and ensure a healthier, more comfortable lifestyle.
What You'll Learn
- Patch Testing: Apply small amounts of fragrances to the skin and observe for reactions over 48 hours
- Patch Test Duration: Longer testing periods may be needed to detect delayed allergic reactions
- Patch Test Sites: Test on the inner elbow, wrist, and back to assess skin sensitivity
- Patch Test Concentration: Vary fragrance concentration to identify the threshold for allergic response
- Patch Test Removal: Carefully remove the patch to avoid irritation and ensure accurate results

Patch Testing: Apply small amounts of fragrances to the skin and observe for reactions over 48 hours
Patch testing is a widely recognized method to identify potential allergies to fragrances and other cosmetic ingredients. This in-office procedure is a safe and effective way to determine which substances may trigger an allergic reaction. Here's a detailed guide on how patch testing works for fragrance allergies:
During patch testing, small amounts of various fragrances and potential allergens are applied to the skin in a controlled manner. The sites chosen for application are typically the inner elbow and the back of the ear, as these areas are less prone to irritation and provide a good representation of the skin's reaction. These patches are left on for 48 hours, allowing the skin to absorb the fragrance and providing a comprehensive assessment. The process involves a series of steps:
First, a panel of common fragrances and potential allergens is selected based on clinical guidelines and patient history. This panel may include ingredients like parabens, preservatives, and common natural allergens. Each fragrance is applied in a small, precise amount to the patch. The patches are then carefully placed on the designated skin areas, ensuring they are secure and in contact with the skin. It is crucial to follow the instructions provided by the testing facility or healthcare professional to maintain consistency and accuracy.
After the 48-hour observation period, the patches are removed, and the skin is examined for any signs of allergic reactions. Reactions can vary and may include redness, itching, swelling, or the development of blisters. The severity and type of reaction provide valuable information about the patient's sensitivity to specific fragrances. For instance, a mild reaction to a particular fragrance may indicate a low sensitivity, while a more severe reaction could suggest a higher likelihood of an allergy.
This method allows healthcare providers to identify fragrances that an individual may need to avoid to prevent allergic reactions. It is a crucial step in managing and treating fragrance allergies, ensuring that patients can make informed decisions about their cosmetic choices and overall skin care routines. Patch testing is a valuable tool in the field of dermatology, offering a precise and controlled approach to assessing fragrance allergies.
Mastering the Art of Fragrance Styling: Tips for a Sensual Signature
You may want to see also

Patch Test Duration: Longer testing periods may be needed to detect delayed allergic reactions
When it comes to identifying fragrance allergies, the patch test is a common and effective method. However, it's important to understand that this test may not always provide immediate results. Allergic reactions can sometimes be delayed, which means that a longer testing period is often required to detect these reactions accurately.
The patch test involves applying a small amount of the suspected allergen to the skin and covering it with a patch. This patch is typically left on for a specified duration, usually 48 hours. While this duration is sufficient to detect immediate reactions, it may not be enough to uncover delayed reactions. Delayed allergic reactions can take several days to appear, and they may manifest as skin redness, itching, or a rash that was not present during the initial test.
To ensure a comprehensive evaluation, it is recommended to extend the patch test duration. Some experts suggest leaving the patches on for 72 hours or even up to 96 hours. This extended period allows for the detection of both immediate and delayed reactions. During this time, it's crucial to monitor the test sites closely and record any changes or symptoms that occur.
In addition to the patch test duration, the frequency of testing can also play a role in identifying delayed reactions. Multiple testing sessions, spaced a few days apart, can help capture reactions that may not appear immediately. For instance, a patient might undergo an initial patch test, then return for a second test a few days later to assess any delayed responses.
It's worth noting that the interpretation of patch test results should always be done by a qualified healthcare professional. They can analyze the findings, considering the duration of the test and the patient's medical history, to determine if a fragrance allergy is present. This process ensures that individuals receive accurate diagnoses and appropriate guidance regarding their fragrance choices.
Mastering the Art of Scent: Candle Fragrance Dos and Don'ts
You may want to see also

Patch Test Sites: Test on the inner elbow, wrist, and back to assess skin sensitivity
When it comes to identifying fragrance allergies, patch testing is a crucial method to determine your skin's reaction to various substances. This non-invasive technique involves applying small amounts of potential allergens to the skin to observe any adverse reactions. The sites chosen for patch testing are essential to ensure accurate results and provide valuable insights into your skin's sensitivity.
The inner elbow, wrist, and back are the recommended areas for patch testing. These sites are ideal for several reasons. Firstly, the inner elbow is a common location for patch testing because it is relatively flat and provides a good surface area for application. This area is also less prone to movement, ensuring that the patch remains in place for the duration of the test. Secondly, the wrist is another suitable site as it is easily accessible and has a thin, delicate skin layer, which can mimic the reaction of more sensitive areas of the body. Lastly, the back is chosen for its larger surface area, allowing for multiple test applications, and it is less visible, reducing the potential for self-induced bias during the test period.
Applying the patch test involves a simple process. A small amount of the fragrance or ingredient to be tested is placed on a sterile adhesive patch, which is then carefully applied to the designated skin site. It is essential to follow the instructions provided by the testing facility or your healthcare professional to ensure the correct placement and duration of the patch. Typically, the patch is left in place for 48 hours, during which time your skin will react if it is sensitive to the substance.
During the test period, it is crucial to avoid any potential irritants or allergens that could interfere with the results. This includes avoiding harsh chemicals, fragrances, and even certain foods that may trigger an immune response. Additionally, maintaining a consistent skincare routine and avoiding excessive moisture or sweating in the test area can help ensure accurate results.
After the 48-hour period, the patch is removed, and the skin is examined for any signs of irritation, redness, itching, or swelling. These reactions can indicate an allergic response to the fragrance or ingredient. It is important to note that patch testing should be conducted under professional supervision to ensure the safety and accuracy of the results. A qualified healthcare provider can interpret the findings and provide guidance on managing and avoiding potential allergens.
Natural Ways to Eliminate Fragrance Oil Stains from Your Clothes
You may want to see also

Patch Test Concentration: Vary fragrance concentration to identify the threshold for allergic response
A patch test is a common method used to identify potential fragrance allergies and determine the concentration of a fragrance that triggers an allergic reaction. This test involves applying a small amount of the fragrance to a patch, which is then placed on the skin for a specified period, typically 48 hours. The concentration of the fragrance used in the patch test is crucial in accurately assessing the threshold for an allergic response.
To perform a patch test with varying fragrance concentrations, you can follow these steps:
- Prepare the Fragrance Solutions: Start by preparing a series of fragrance solutions with different concentrations. This can be done by diluting the fragrance oil or extract with a suitable solvent, such as alcohol or water. Create a range of solutions, starting with a highly concentrated one and gradually diluting it to create less concentrated versions. For example, you might have 10%, 5%, 2.5%, and 1% solutions of the fragrance.
- Apply the Patches: Using sterile gauze or adhesive tape, apply small amounts of each fragrance solution to separate patches. Ensure that the amount applied is consistent across all patches to maintain uniformity. Place these patches on the inner elbow or the back of the ear, areas that are less visible and less prone to irritation.
- Monitor for Reactions: Leave the patches in place for the recommended duration, typically 48 hours. Observe the skin carefully during and after this period. Look for any signs of allergic reactions, such as redness, itching, swelling, or blisters. Note the time of appearance and the severity of the reaction for each fragrance concentration.
- Record and Analyze Results: Document the reactions for each fragrance concentration. The goal is to identify the lowest concentration that triggers an allergic response. If no reaction is observed at a particular concentration, you can further dilute the fragrance to test even lower concentrations. The concentration at which the allergic reaction first occurs is considered the threshold.
- Interpretation: By varying the fragrance concentration, you can pinpoint the specific level at which an individual's immune system reacts adversely. This information is valuable for understanding the sensitivity of the person to different fragrances and can guide recommendations for fragrance avoidance or the use of hypoallergenic alternatives.
This method of patch testing with varying concentrations allows for a more comprehensive assessment of fragrance allergies, helping individuals make informed choices about their skincare and fragrance products. It is a precise way to identify the exact fragrance threshold that triggers an allergic reaction, ensuring that individuals can take appropriate measures to avoid potential allergens.
Triton X-100: A Fragrance Carrier?
You may want to see also

Patch Test Removal: Carefully remove the patch to avoid irritation and ensure accurate results
When conducting a patch test to identify fragrance allergies, the removal process is crucial to ensure accurate results and minimize potential irritation. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to carefully remove the patch:
- Timing: Allow the patch to remain on the skin for the recommended duration, typically 48 hours. This period is essential for the skin to react to the fragrance, if it is an allergen. Removing the patch too early might not provide reliable results.
- Gentle Removal: Carefully peel off the patch from the skin. Start at one end and gently lift the patch, avoiding any sudden or forceful pulling. The goal is to remove it slowly to prevent irritation and potential damage to the skin. If the patch is difficult to remove, you can slightly wet the skin around the patch to help it come off more easily.
- Observe and Document: After removing the patch, inspect the test area for any signs of irritation, redness, or swelling. Note the appearance of the skin, including any changes in color or texture. This information is valuable for interpreting the test results and understanding your skin's reaction.
- Clean the Area: Once the patch is removed, clean the test site with mild soap and water to ensure no residue remains. This step is important to prevent any potential irritation or allergic reactions from the patch material.
- Avoid Touching: Refrain from touching or scratching the test area for at least 24 hours after removal. Irritation from the patch removal process should be minimal, but it's essential to avoid further stimulation of the skin, which could lead to false positives or unnecessary discomfort.
- Record Observations: Document your observations, including the time of patch removal, the appearance of the skin, and any symptoms experienced. This record will assist healthcare professionals in interpreting the test results and providing appropriate advice regarding fragrance avoidance.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the patch test removal process is gentle, accurate, and free from unnecessary irritation, contributing to a reliable assessment of fragrance allergies. It is always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for guidance and interpretation of test results, especially when dealing with potential allergies.
Creating Fragrant Bath Salts: Oil-Based Aromatics
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To test for a fragrance allergy, you can perform a patch test. This involves applying a small amount of the fragrance to your skin, typically on the inside of your elbow or behind your ear, and covering it with a bandage. Leave it for 48 hours, and then check for any signs of irritation, redness, or a rash. If you experience any allergic reactions, it's best to avoid the fragrance and consult a healthcare professional for further advice.
While patch testing is a common and effective method, at-home tests are also available. You can purchase fragrance allergy test kits from pharmacies or online stores. These kits usually include a set of patches with different fragrances and instructions on how to apply and read the results. However, it's important to note that at-home tests may not be as accurate as professional patch tests, and consulting a doctor is recommended for a more reliable diagnosis.
Fragrance allergies can manifest in various ways, including skin reactions such as hives, itching, swelling, or a rash. Some people may also experience respiratory issues like sneezing, runny nose, congestion, or difficulty breathing. In more severe cases, an allergic reaction can lead to anaphylaxis, a medical emergency requiring immediate attention. If you suspect an allergy, it's crucial to seek medical advice to ensure proper diagnosis and management.







