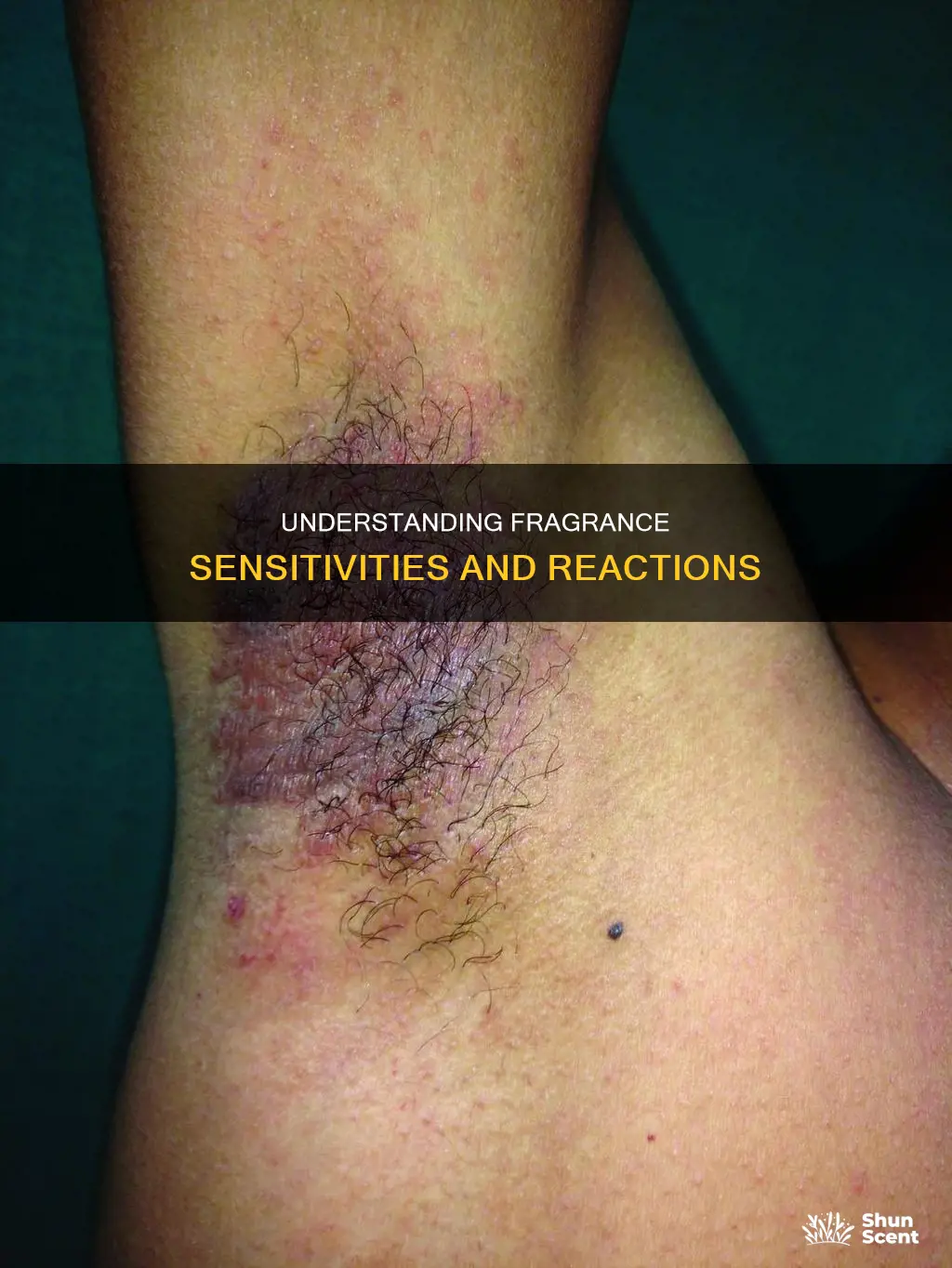
Fragrances added to soaps, lotions, makeup, perfumes, and colognes can cause an overreaction by the immune system. This happens when the body identifies an ingredient in the perfume as a foreign substance and releases an inflammatory reaction to fight it off. The most common symptom of this reaction is an itchy, red rash on the skin, called contact dermatitis. Up to 4.5% of the general adult population may be allergic to fragrance materials.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cause of reaction | The body identifies an ingredient in the perfume as a foreign substance |
| Reaction | The body releases an inflammatory reaction to help fight off the substance as if it's a bacterial or viral invader |
| Symptoms | Itchiness or a rash |
| Type of allergy | Chronic condition involving abnormal immune reactions to ordinarily harmless substances in fragranced products |
| Occurrence | When certain fragrance components called allergens come into contact with the skin |
| Reaction | The immune system reacts by making protective proteins called antibodies to defend against the allergens |
| Result | Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) |
| Symptoms | Itchy, red rashes on the skin that has been directly exposed to the irritating substance |
| Testing | Skin patch testing |
What You'll Learn

Fragrance allergies and the immune system
Fragrance allergies are a chronic condition involving abnormal immune reactions to ordinarily harmless substances in fragranced products. When you have allergies, your body has a specific immune system response to an ingredient or a chemical in the perfume that causes the reaction. This means that your body identifies the ingredient in the perfume as a foreign substance. Then, it releases an inflammatory reaction to help fight off the substance as if it’s a bacterial or viral invader. This immune system response usually develops over a course of days and manifests as itchiness or a rash.
Up to 4.5% of the general adult population may be allergic to fragrance materials. A fragrance allergy typically occurs when certain fragrance components called allergens come into contact with the skin. This causes the immune system to react by making protective proteins called antibodies to defend against the allergens. This inflammatory response leads to allergy symptoms. In most cases, the reaction results in allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), an itchy rash that shows up on the skin that has been directly exposed to the irritating substance.
Skin allergies to fragrance ingredients frequently involve the skin of the face, hands, or armpits. In some cases, exposure to certain substances can cause irritation, which does not provoke the immune system. If you’re intolerant, as opposed to allergic, to a component of a fragrance, it will likely take much more of that component to elicit a reaction.
To definitively understand what is causing the reaction and whether or not it is related to fragrance compounds, you will have to undergo skin patch testing. Patch testing is generally to see whether a substance is causing allergic skin inflammation (allergic contact dermatitis).
Traveling with Wax Fragrance Cubes: Allowed or Not?
You may want to see also

Allergic contact dermatitis
Fragrances added to soaps, lotions, perfumes, and colognes can cause an overreaction by the immune system. The fragrance triggers the immune system to release chemicals that cause allergy symptoms. The most common symptom is an itchy, red rash on the skin, called contact dermatitis.
When you have allergies, your body has a specific immune system response to an ingredient or a chemical in the perfume that causes the reaction. This means that your body identifies the ingredient in the perfume as a foreign substance. Then, it releases an inflammatory reaction to help fight off the substance as if it’s a bacterial or viral invader. This immune system response usually develops over a course of days and manifests as itchiness or a rash.
In most cases, the reaction results in allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), an itchy rash that shows up on the skin that has been directly exposed to the irritating substance. Skin allergies to fragrance ingredients frequently involve the skin of the face, hands, or armpits.
To definitively understand what is causing the reaction and whether or not it is related to fragrance compounds, you will have to undergo skin patch testing. Patch testing is generally to see whether a substance is causing allergic skin inflammation (allergic contact dermatitis). Patch testing does not involve needles. Instead, allergens are attached to patches that are placed on the skin of your arm or back. During the test, your skin is exposed to extracts of substances that can cause contact dermatitis. You wear the patches for 48 hours.
Using Fragrance Oils: Wax Warmer Tips and Tricks
You may want to see also

Fragrance allergy symptoms
Fragrance allergies are abnormal immune reactions to ordinarily harmless substances in fragranced products. Up to 4.5% of the general adult population may be allergic to fragrance materials. Fragrance allergies typically occur when certain fragrance components called allergens come into direct contact with the skin. This causes the immune system to react by making protective proteins called antibodies to defend against the allergens. This inflammatory response leads to allergy symptoms.
The most common symptom is an itchy, red rash on the skin, called contact dermatitis. This rash usually appears on the face, hands, or armpits, where the skin has been directly exposed to the irritating substance. In rare cases, a fragrance allergy can cause anaphylaxis or a serious allergic reaction.
To definitively understand what is causing the reaction and whether or not it is related to fragrance compounds, you will have to undergo skin patch testing. Patch testing is generally used to see whether a substance is causing allergic skin inflammation (allergic contact dermatitis). During the test, your skin is exposed to extracts of substances that can cause contact dermatitis. You wear the patches for 48 hours, and skin responses are evaluated after 48 hours and again at between 72 and 96 hours for delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
Are Plug-In Fragrances Safe for Pets?
You may want to see also

Fragrance allergy diagnosis
Fragrance allergies are abnormal immune reactions to ordinarily harmless substances in fragranced products. They are chronic conditions that generally cause symptoms on the skin, such as an itchy, red rash, known as allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). This can be treated with medication. Up to 4.5% of the general adult population may be allergic to fragrance materials.
When you have allergies, your body has a specific immune system response to an ingredient or a chemical in the perfume that causes the reaction. This means that your body identifies the ingredient in the perfume as a foreign substance and releases an inflammatory reaction to help fight it off as if it were a bacterial or viral invader. This immune system response usually develops over a course of days and can manifest as itchiness or a rash.
The fragrances added to soaps, lotions, face and eye makeup, perfumes, and colognes can also cause an overreaction by the immune system. The fragrance triggers the immune system to release chemicals that cause allergy symptoms.
To definitively understand what is causing the reaction and whether or not it is related to fragrance compounds, you will have to undergo skin patch testing. Patch testing is generally to see whether a substance is causing allergic skin inflammation (allergic contact dermatitis). Patch testing does not involve needles. Instead, allergens are attached to patches that are placed on the skin of your arm or back. During the test, your skin is exposed to extracts of substances that can cause contact dermatitis. You wear the patches for 48 hours. Skin responses are evaluated after 48 hours and again at between 72 and 96 hours for delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
Fragrance Outlet: Cheap Scents, Explained
You may want to see also

Fragrance allergy treatment
If you think you might have a fragrance allergy, you should consult a healthcare provider. An allergist can confirm the diagnosis.
In order to definitively understand what is causing the reaction and whether or not it is related to fragrance compounds, you will have to undergo skin patch testing. Patch testing is generally to see whether a substance is causing allergic skin inflammation (allergic contact dermatitis). Patch testing does not involve needles. Instead, allergens are attached to patches that are placed on the skin of your arm or back. During the test, your skin is exposed to extracts of substances that can cause contact dermatitis. You wear the patches for 48 hours. Skin responses are evaluated after 48 hours and again at between 72 and 96 hours for delayed hypersensitivity reactions.
In the meantime, you can try to avoid fragranced products. This can be difficult, as many companies can simply put "fragrance" on their perfumes to represent a hundred or more chemical compounds. However, you can try using cleaning solutions like baking soda and vinegar, which are more smell-friendly than many pre-packaged products. You can also get rid of air fresheners and open windows for ventilation instead.
Dove's Fragrance: What's the Scent?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fragrance can cause an overreaction by the immune system. The immune system releases chemicals that cause allergy symptoms.
The most common symptom is an itchy, red rash on the skin, called contact dermatitis.
You can undergo skin patch testing to see whether a substance is causing allergic skin inflammation.
Up to 4.5% of the general adult population may be allergic to fragrance materials.







